GCP Data Engineer : Cloud Storage

Storage Services in GCP
This blog will focus on Cloud Storage service in GCP.
Object Storage ( Buckets ) : To store unstructured data and for archival use-cases.
Instance Storage ( Persistent Disks ) : To work with VMs, Kubernetes Clusters
SQL ( Cloud SQL, Cloud Spanner ) : For Relational DB use-case and for transaction support
NoSQL ( BigTable, DataStore ) : For storing non-relational data
Analytic ( Cloud BigQuery ) : For Data warehousing
Cloud Storage
Cloud Storage helps in storing unstructured data , by having files or images been stored into buckets in GCS.
Login to cloud console : https://console.cloud.google.com/storage and move to Storage service section.
While creating a bucket, below are the storage class type options provided

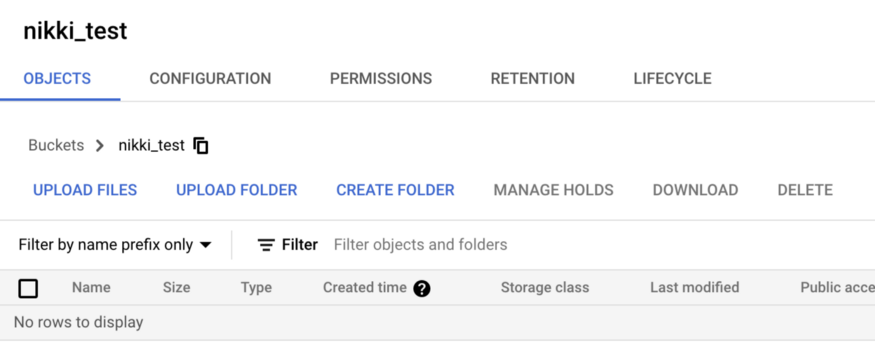
Once bucket got created, user can login to the console to upload files or folders to move into the bucket.
Loading Data into Storage
For less Volume of data, we can use one of the following
gsutil : command line utility to copy files into bucket, to create bucket and to move files. Activate Cloud Shell from Cloud Console ( appear on the right corner with image “>”
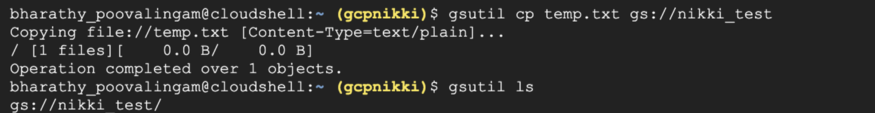
Cloud Console
API
For Bulk and large volume of data, we can use
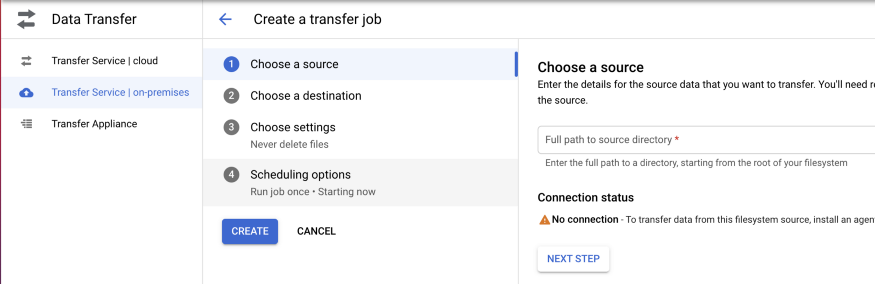
Cloud Storage Transfer : Moving data from On Premises and other cloud services, to move data between cloud storage buckets, transfer more than 1Tb from on-premises. Supports one-time and recurring transfers.
Transfer Appliance : High Capacity storage server, to move large volumes of data (100 Tb)
Security
Data stored in GCP is encrypted by default. While creating bucket, under advanced settings, you can chose the option to encryption as below.

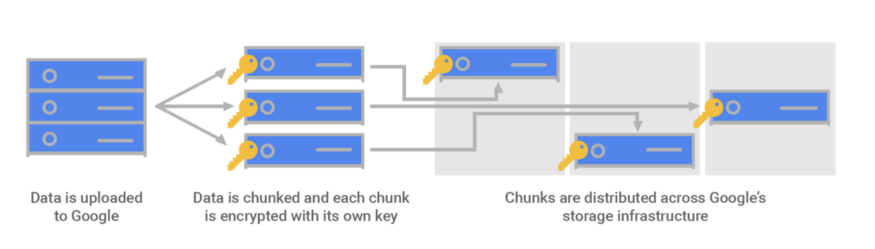
Data uploaded into GCP is divided into multiple data chunks, each been encrypted with its own key ( Data Encryption Key : DEK ) and data encryption keys are been encrypted using Key Encryption Key ( KEK ) which gets stored in KMS ( Key Management Service )
ACLs
Uniform Bucket Level Access : Recommended, uses IAM (Identity and Access Management ), permission at Bucket Level
Fine-grained Access : Uses ACLs, permission apply at both Bucket and Object Level

Signed URLs
Time Limit read or write access to an object ( short-term access )
Allow access to those without IAM authorizations. Generate signed url comprise of two steps
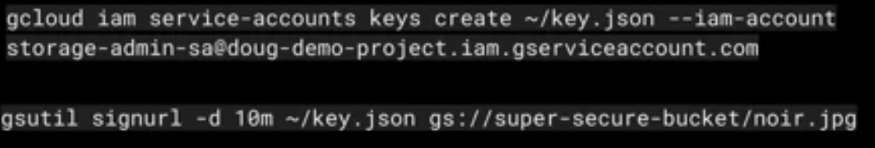
Creating Service Account Key with relevant permission
Using gsutil command to generate the url passing the service account key as json and the time for url to be accessed using param : “-d”
Signed Policy Documents
Specify what can be loaded to a bucket with a form post
Allow greater control over size,content type and other upload characteristics than signed urls.
Lifecycle Policy Management
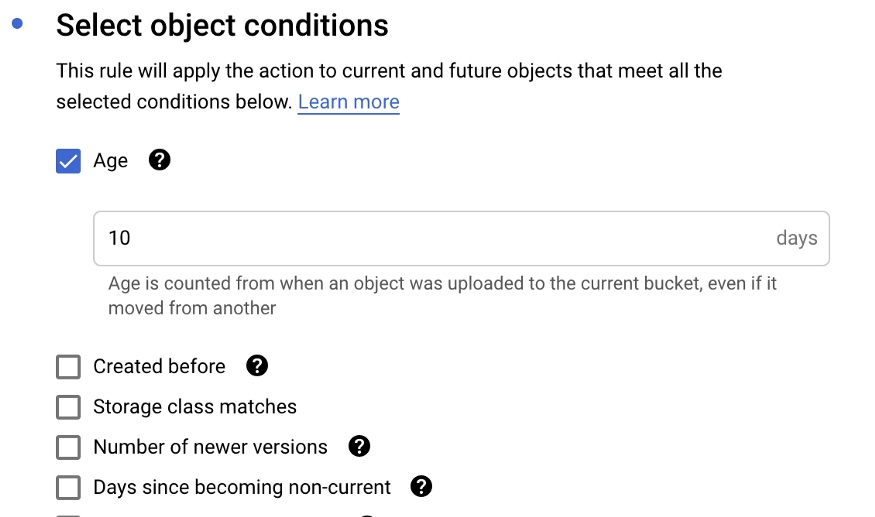
It consist of Actions and Conditions. What is the action to be performed on the bucket when the condition met
Action can be moving object from one storage class to another one

Actions executed when condition applies eg : Change Storage class based on age, Delete object based on date, Purge versions etc
Happy Learning !
Bharathy Poovalingam



